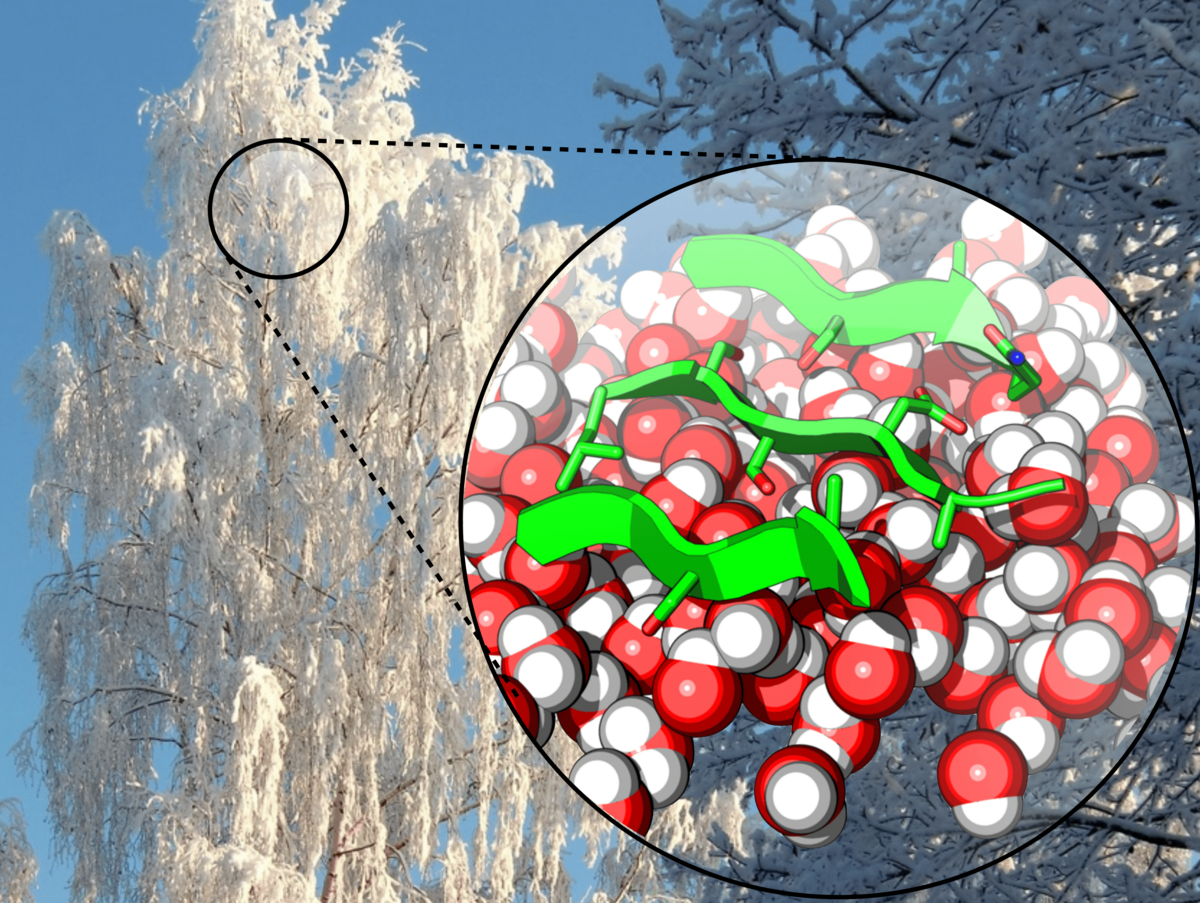
Certain bacteria can stimulate the growth of ice and snow better than any other material known. Using their specialized ice nucleating proteins (INPs) they attack plants with frost damage and, when airborne, drive cloud seeding and influence global precipitation. Nevertheless, the mode of action of these INPs have largely remained a mystery. This lack of knowledge can be traced back to difficulty of studying phase transitions and protein structure at the very interface between monolayers of proteins and water.
In SurfLab, we study the structural basis of ice nucleation by proteins. How do INPs order themselves and the water molecules to form ice? We use a combination of sum frequency generation, cryo electron microscopy, and computer simulations to study INPs in action, both on model water surfaces and in realistic water aerosol chambers.
Research funding: ERC and BioIce
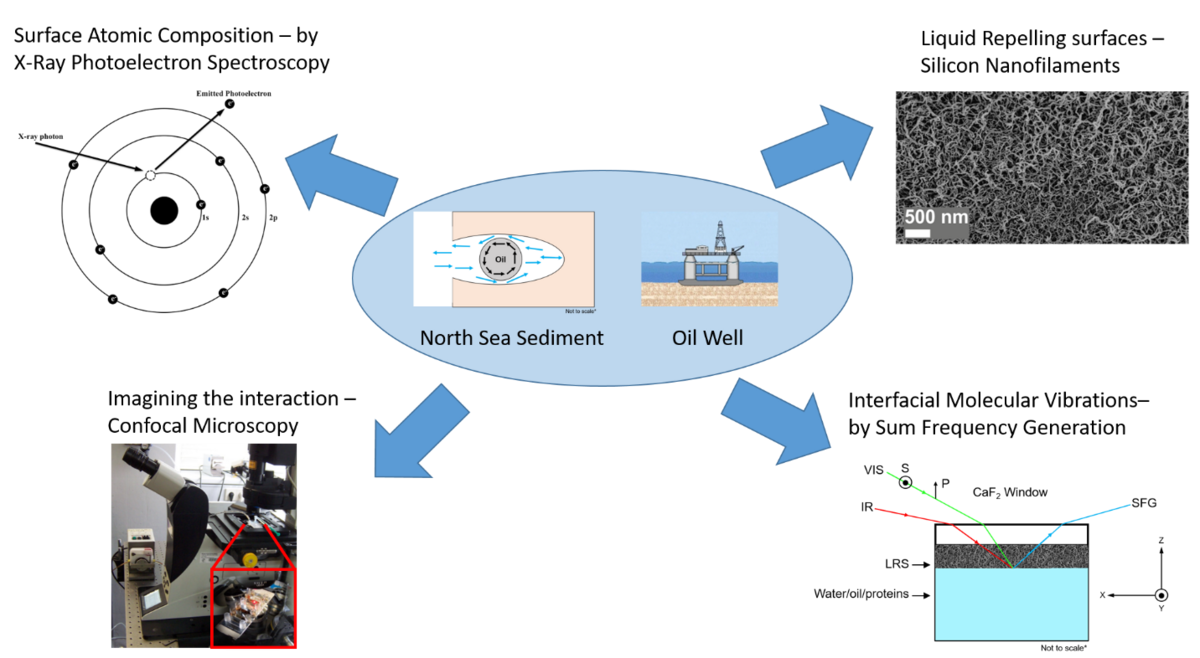
We wish to use spectroscopy and microscopy to screen for smart water formulations for recovering oil from chalk sediments as well as modifying the surface of wells with liquid repelling surfaces to reduce fouling, scaling, corrosion when dealing with oil from the North Sea. We wish to also identify which molecules are present at the oil-water-sediment interface and then determine which molecules are vital for oil-water-chalk interactions. We have two main challenges with our project. The first is that the molecular interfacial properties of the oil-water-sediment interfaces are unknown. Second, oil flow within tubes and wells is hindered by friction at the tube material surface and the surface is susceptible to biofouling, scaling and corrosion. To overcome the challenges we need to both know how the molecules are interacting with each interface and be able to deposit a coating on pipes and wells that can reduce biofouling, scaling and corrosion. In short, these surfaces are unique because they rely on interactions that are unique to every molecule present at the surface.
Research funding: DHRTC
Amino acids are chiral molecules and come in both left-handed and right-handed forms. Nevertheless, virtually all living organisms on Earth are exclusively made of left-handed amino acids and nobody knows why. Our project “Shining Light on the Origin of Life” studies the ultraviolet photolysis of aqueous amino acids in order to assess if asymmetric photolysis in the pre-biotic oceans could be the reason for the homochirality of living organism on Earth. For the hypothesis of amino acid homochirality by asymmetric photolysis to be true, it is desirable, although not a strictly necessary requirement, that the homochirality can be obtained for all amino acids by illuminating them at the same wavelength. This condition is fulfilled, when the carboxyl acid group common to all the amino acids is photolysed by UV light at a wavelength around 200 nm. The 200 nm excitation wavelengths is known to correspond to the lowest excitation energy of the carboxyl group and pertains to a nO -> πCO* transition from the lone-pair on the carbonyl oxygen to the antibonding πCO-valence orbital. The strong absorption band of water beginning around 195 nm precludes photolysis of aqueous amino acids through states with higher excitation energies, and illumination at 200 nm is thus the only common path for asymmetric photolysis of all amino acids.
The photolysis of the amino acids is studied by our state-of-the-art Femtosecond laser facility.
Research funding: Villum Foundation
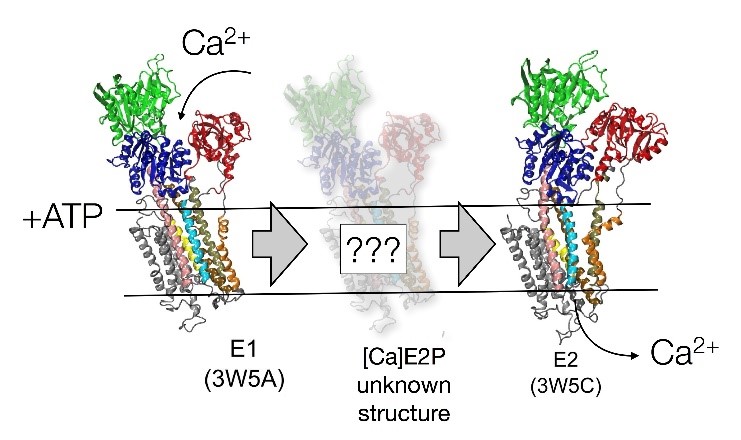
ATPases are specialized proteins that transport calcium ions against steep concentration gradients across cell membranes. Calcium signaling depends on the twenty thousand-fold concentration difference across the cell membrane – one of the steepest biomembrane gradients known.
A recent study has shown that the ATPase cycle is based on transient states, which ensure the irreversibility of the ion translocation.
Within this project UV pump IR probe Sum Frequency Generation (SFG) spectroscopy and single molecule Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (smFRET) will be combined to map out the dynamical landscape and determine the structure of transient states related to the Ca2+ ion pump mechanism in plasma membrane calcium.
Research funding: Lundbeck Foundation
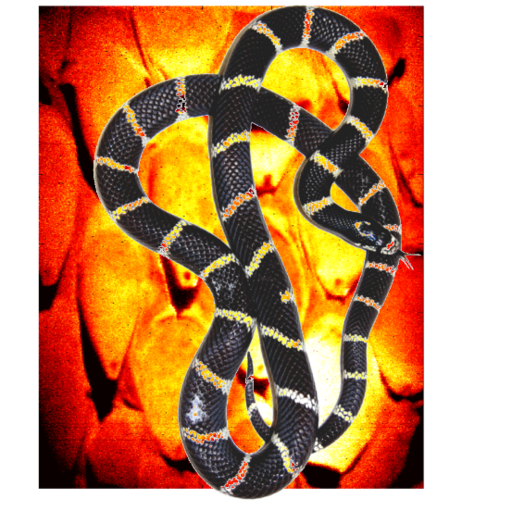
Snakes are in constant contact with their surroundings during slithering locomotion. The scales of the snake are therefore specialized for movement over various types of surfaces. A recent study has shown that a nanometer-thin layer of lipids covers the scales of the California King snake. This lipid layer has a higher degree of order on the ventral (belly) compared to the dorsal (backside) of the snake, which reduces friction, provides lubrication, and thereby improves the snake’s movement.
In SurfLab, we are interested in understanding the surface chemistry of snakes: Is the surface chemistry different for snakes living in different habitats? Will the surface chemistry vary for different environments such as water, sand, or trees? We study the outermost few nanometers of the scales with sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy (SFG) in combination with near-edge x-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) microscopy. We follow variations across the scales in terms of molecular bonds, orientation and functional groups, and relate the molecular picture to scale performance.
Research funding: FNU

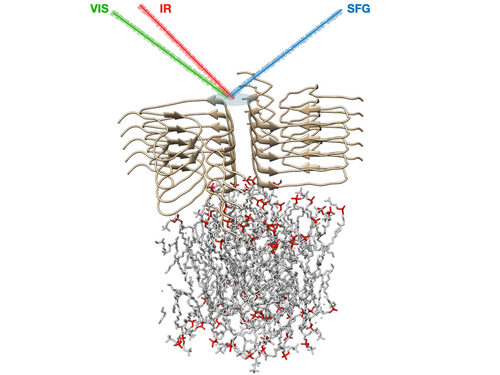
The formation of amyloid aggregates (protein oligomers and fibrils composed of intermolecular β-sheets) is currently known to be related to approximately 50 disorders, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and type-II diabetes. In the case of Parkinson’s disease, amyloid aggregates composed mainly of α‑synuclein (αS) are found in inclusion bodies that are an import hallmark for the disease. Over the past decade, increasing evidence has emerged that suggests that oligomeric aggregates formed by αS are the cause of neuronal cell death leading to Parkinson’s disease. Other recent studies implicate that oligomerization and aggregation are greatly enhanced by the presence of lipid membrane, and that genes that encode for certain types of lipids strongly influence the development of the disease. However, there is little known about the molecular structure of the transient oligomers that αS forms near lipid membranes, and there are still no drugs known that can stop this process in vivo.
This lack of knowledge is partly caused by the fact that it is challenging to resolve the conformation of these interfacial structures: in most experimental techniques the signal of proteins at the surface is several orders of magnitude smaller than a spectrally similar signal of proteins that are unbound or in solution. Surface-specific molecular-level information that would be valuable for the developments of drugs against toxic-oligomer formation, can be provided by SFG spectroscopy. And while most conventional techniques can only characterize the structure of certain αS species (e.g. in solution, as mature fibrils or in crystalline form), by recording SFG spectra in various spectral regions, the αS conformation during the whole aggregation process can be monitored, from the monomeric, via the oligomeric into the fibrillar phase.
Within this project funded by the Lundbeck Foundation, we use our surface-specific spectroscopic experience and equipment to reveal the molecular basis of Parkinson’s disease, by answering questions like: why does human αS cause Parkinson’s disease, while whale or elephant variants appear not to cause the disease? And how do the lipids for which the Parkinson’s-related genes encode affect the amyloid aggregation of αS? By making use of the state-of-the-art SFG laser setup, and combining the recorded spectra with additional constraints from cryo-EM to perform spectral calculations, we hope to answer these, and many other molecular questions with respect to amyloid-related diseases. The project is a collaboration with the AU groups of Daniel Otzen and Thomas Boesen.
Research funding: Lundbeck Foundation